The Core
Think your core muscles are just a ‘six pack?’ You’re wrong! Learn more about your core and it’s importance in movement.
Written by Jenny Devlin, MSK Physiotherapist and Specialist Women’s Health Physiotherapist at Physio Effect
The Core
What do you think of when you hear the word ‘core’?
For most people, they think of the rectus abdominis muscles, or the “six pack muscles”, but the core is so much more than that!
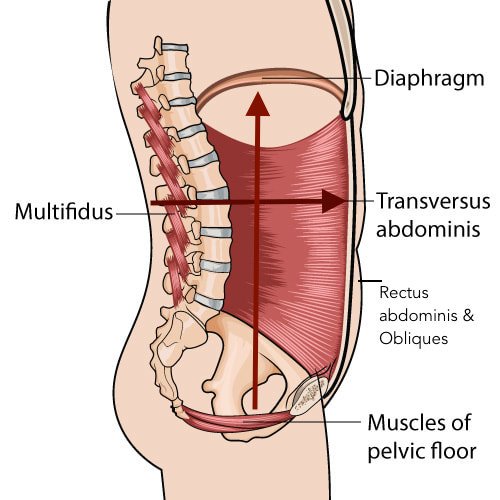
The core is actually a full canister that comprises a top, bottom, front and back. Respectively, these are:
The diaphragm
The pelvic floor
The transversus abdominis (deep stomach muscles)
The multifidus (deep back muscles)
Abdominal canister illustration courtesy of ‘The Wellness Blog for Women.’
These muscles work all the time to hold us upright and provide a base from which other muscles can operate. People will often tell us they ‘have no core’ which simply can’t be true or they would be a floppy noodle! What they mean is that they have forgotten how to tune in to activate their core and the good news is that this can be trained.
Our core canister houses our fluid and organs and is responsible for controlling pressure within the system, namely intra-abdominal pressure (IAP). IAP helps our ribs and spine stay in place and is the central mechanism from which we produce strength and stability. Since the muscles surround the canister, they are in prime position to help to control the pressure. IAP changes to match the task we are looking to perform and without a strong inner unit, it is challenging to keep our bodies moving and functioning effectively.
At Physio Effect we can offer you a path back to exercise safely after pregnancy.
Why do i have weakness in my core?
There are many things which can contribute to the core functioning less optimally - it could be the way you train or perform your sport, from being overweight or just a lack of body awareness of how to engage the correct muscles. In particular, pregnancy can lead to dysfunction as the muscles have been stretched out over nine months to accommodate the baby and then afterwards we often just hope they will go back to doing what they did before. Strength and coordination often need to be retrained and, while traditional abdominal exercises are great, it is important to ensure we have the deep core muscles working efficiently before we layer on the larger muscle groups. When we don’t have good core control, it can lead to injuries anywhere in the body such as the low back or the shoulder.
It is normal to have a diastasis rectus abdominus (abdominal separation) following pregnancy but when the pressure is not well controlled, we see doming at the linea alba (midline connective tissue). If we can work to control the IAP with the core muscles, we can minimise this doming and increase overall strength and performance since we are not losing pressure at our core canister.
Illustration of Abdominal Separation courtesy of Cleveland Clinic.
What can I do to strengthen my core?
It is important to spend time connecting to the core and learning how to coordinate the breath, pelvic floor and deep abdominal and low back muscles before adding more challenging exercises to your program. Our physiotherapists can provide you with some targeted core exercises that are specific to your needs. You could also consider our Clinical Pilates, Pregnancy Pilates or Postpartum Pilates Classes to strengthen your core.
To find out more, give us a call or book in online.
Proprioception Drills for Hill Runners
Trail and hill running as a sport is demanding on our bodies. Common injuries are often as a result of overloading an area of the body not able to meet the demands placed on it, particularly as running is a repetitive, high-impact activity. Here are some of our favourite exercises to help improve strength, proprioception and build fatigue resistance to improve your running economy.
written By Mariam Kilpatrick - Physiotherapist and Ultra-runner
Trail and hill running as a sport is demanding on our bodies. Common injuries are often as a result of overloading an area of the body not able to meet the demands placed on it, particularly as running is a repetitive, high-impact activity. Here are four of our favourite exercises to help improve strength, proprioception and build fatigue resistance to improve your running economy.
STEP UP
What you will need…
A Bench or box that is knee height.
Technique Tips
Try NOT to push through your back leg.
Step up with the weight primarily on your heel.
Maintain a knee window i.e. knees on either side of your midline.
Perform 8-12 reps each leg, aim to perform 5-6 sets with a max of 30s rest between each one.
2. SINGLE LEG BALANCE
What you will need…
An unstable surface to balance on i.e. a bosu ball, wobble board or cushion.
Technique Tips
While balancing on one leg try;
Writing the letters of the alphabet with the other.
To draw a clock face.
Closing your eyes.
Perform 1 minute each leg, aim to perform 2-3 sets with a max of 30s between each one.
3. POLEQUIN STEP UP
What you will need…
A slant/decline board OR
A small block placed beneath your heel to elevate it, while standing on a step. This puts your foot into a decline position.
Technique Tips
Keep your weight on the block.
Lightly tap your other heel to the floor.
Maintain a knee window i.e. knees on either side of your midline.
Perform 8-12 reps each leg, aim to perform 5-6 sets with a max of 30s rest between each one.
4. TRAMPETTE BALANCE
What you will need…
A trampette
OR
Your child’s back yard trampoline.
Technique Tips
Aim to land on the same spot, don’t bounce all over the place.
Don’t let you knee fold inwards.
Spend a minute on each leg, aim to work 5-6 sets or work to fatigue.
The Glasgow Running Clinic
If you’d like to improve your running technique or are keen to prevent or return from injury, Physio Effect offer a bespoke running analysis service to get you operating at peak performance. Call our reception team on 0141 230 4766 to find out more and schedule your appointment.
Animal flows - What, How and Why?
Animal flows are a great addition to any exercise plan, warm up routine or injury prevention plan. Learning to move like a monkey, frog, or bear helps to build full body strength, mobility and motor control which in turn will make you a more awesome human and less prone to injury. This blog with video tutorials will explain what these movements are, how to utilise them and why you should should be doing them
What are Animal Flows?
Animal flows essentially refer to movement and exercise patterns where we imitate different types of animals such as bears, monkeys, frogs or lizards. Moving in these patterns can be very challenging, especially for the stiff & inflexible among us, but can also be really fun & provide significant benefits.
Deep Squat
Practicing animal flows can help improve strength, flexibility, mobility and overall motor control which in turn will help to make you a better functioning human and less at risk of injury. These movements can really challenge us in unconventional ways demanding our joints and muscles learn to control movement in patterns and ranges we would rarely otherwise practice. They can provide a great way to warm the body up in preparation for other forms of exercise or can even act as a stand alone training session. Once you have tried some of these movements for a few minutes you will understand why!
Where do I start?
As with all areas of training and exercise when attempting something new or different our advice is always start slow and work safely within your own levels of capability. Never push through pain or injury and if in doubt about whether this is appropriate for you please seek advice from a qualified professional.
Very few people will be able to perform controlled animal flow movements perfectly or even well at the beginning. When incorporating these kinds of exercises with my patients it’s essential we first establish their base level where they feel safe to practice but also feel that it is challenging. I would advise starting with getting comfortable in the static positions required as the foundation for the movement. In this post we will look at 2 positions - Deep Squat & A-Frame (Downward dog). These are the foundation starting postures for progression onto the animal movements monkey, frog and bear.
Deep Squat
The squat is a great foundation exercise for strength and mobility in the lower limbs and yet for so many people it is a real area of weakness and frustration. A lot of us slowly lose our ability to sit into a deep squat mainly through neglect and lack of practice combined with our static and sedentary western lifestyles. We become weak, stiff and tight and can no longer control the range of motion required to allow a deep squat. We rarely challenge ourselves to sit into a deep squat position let alone spend time exploring and improving on our range and control in this position. So first things first lets get a measure of your baseline squat function - check out this video and see how you get on.
It may take weeks or months of work to improve your squat mobility and that’s okay. For a more detailed look at improving your hip and back mobility please click the links to see our previous blog posts on these areas. You can use these routines alongside your deep squat holds to improve your squat function.
If you feel up to increasing the mobility challenge of your deep squat lets check out this next video requiring some active hip rotation movements at the bottom of the squat - a great way to improve your range of motion and strength.
I would recommend slowly building these exercises into your routines, aim for 20-30 second rounds initially performed for 3-4 sets thereby accumulating 2-3 minutes in the deep squat. Try this at least 2-3 times per week. Long term the idea is to become comfortable spending longer periods in the deep squat and find it relatively easy to perform movements from this position. Try to build up to 5 minutes total in the deep squat per day of practice over several weeks.
Monkey & Frog Mobility
These animal flow progressions are suitable once you have a comfortable squat allowing you to sit at least to parallel depth without the need of hand support. Don’t worry if you’re not there yet, keep practicing the squat, back and hip mobility exercises and you can move on to these once you feel confident.
These exercises are difficult and physically demanding but the pay off of regular practice will be improved squat mobility, increased lower limb strength and motor control with an associated reduced injury risk in these areas. Give each of these a try and see how you get on.
Add these to your regular practice at least 2-3 times per week initially
Begin with 20-30 second rounds aiming to build up to 1-2 minutes or longer
Look to accumulate time in the positions - Try a 5 minute timer & while stopping for breaks when required, try to spend as much time actively moving in these flows
Ideally we want to develop a relaxed freedom of movement where you can drop comfortably into a deep squat and easily move through monkey and frog patterns. You can mix and match the movements to create variation in the flow and challenge your strength and mobility through mixed planes of movement. Don’t expect overnight success but as with all training with hard work and consistent practice you should be able to improve allowing you to move better and feel better.
A-Frame (Downward Dog)
This stretch position is probably best known in yoga circles, most people will of at least heard of the Downward Dog. Another term we will use is A-Frame which refers literally to the fact we are trying to get our body into a position whereby it looks the a capital letter ‘A’. This position is another staple in many exercise forms and for good reason, it challenges the flexibility and strength of our body in many areas. The shoulders, back, hips, knees and ankle joints will be tested and for many people deficiencies in strength and range of movement will limit the quality and range available in attempting this position.
For many of us just attempting this posture will be tough and tiring. A lot of you will be feeling significant resistance in the backs of the legs (hamstrings and calves) and through the shoulders and upper back. Build slowly and increase the time spent in the stretch as you feel able, again looking to improve on your own current baseline level. Before attempting bear movements from this position we can work on a couple of simple variations which are shown in the video - slow marching on the spot and active shoulder extension pushing the head and shoulders through. Let’s give it a try and see how you get on.
Bear Movement Flows
The bear crawl can be utilised as a full body exercise to develop strength, flexibility and control in many areas. It is challenging and will take time to develop the skill and movement control required to perform it well but as with all these exercises your only goal should be to steadily improve on your own current baseline level. Once you have developed some comfort and control with the A-Frame stretch the first Bear Crawl movement we will try is with straight arms and straight legs as demonstrated in the video below. The key here is control so take your time and just do what you can, even if it’s only a few seconds initially, you can build on that. Let’s give it a go.
In the next video we demonstrate a number of bear crawl variations to give you some more options to explore. Depending on your own levels of mobility and strength you may find some options easier and others harder but it is great to play around and explore a variety of positions to find any weaknesses or restrictions and ensure a variety of stimulus is achieved. The key is to safely work on your own issues and don’t be afraid to explore positions that are challenging as long as you do so gradually.
Add these to your regular practice at least 2-3 times per week initially
Try:
Straight arms & legs
Bent arms, straight legs
Bent arms, bent legs
Straight arms, bent legs
Begin with 20-30 second rounds aiming to build up to 1-2 minutes or longer
Move forwards, backwards and sideways
Look to accumulate time in the positions - Try a 5 minute timer & while stopping for breaks when required, try to spend as much time actively moving in these flows
Summary
In summary adding animal flow movement practice into your regular exercise routines or habits can have significant physical benefits by helping to improve full body strength, mobility and motor control. It is a challenging but fun way to mix up your normal exercise routines and pushes your body to explore a variety of joint postures and positions that are not routinely trained or strengthened. This variety of stimulus will help to ensure strong and healthy muscle and joint function. Enjoy exploring and playing with these movements and ultimately you can learn to move better & feel better.
Thank You
Thanks for taking the time to read this guide, we hope you find it useful. Please share with anyone who might benefit and if you have any questions comment and let us know. Please subscribe to our mailing list to receive more interesting and useful blogs. Good luck and remember to move better & feel better